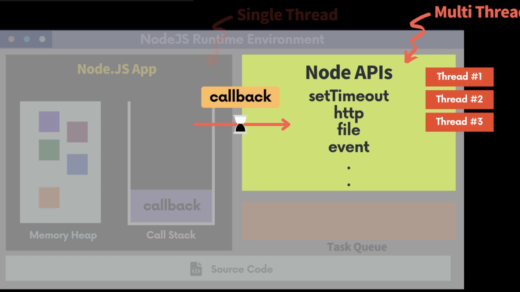
app.js의 기본 뼈대 잡기!
우선 시작 전 필요한 API 들에 대해 정리한다.
- API 정의
- API spec : https://www.notion.so/API-Spec-Tweets-b04541cf06f84b83bf4891abfaa27d03
- postman : https://documenter.getpostman.com/view/9223369/UVsJvSME
필요한 미들웨어 / 라우터를 다 연결해준다.
import express from 'express';
import morgan from 'morgan';
import cors from 'cors';
import helmet from 'helmet';
import 'express-async-errors'; // express 5 이전 비동기 에러 캐치용
const app = express();
app.use(express.json()); // body json 파싱
app.use(morgan('tiny')); // 호출 로그 미들웨어
app.use(cors()); // CORS 처리
app.use(helmet()); // CORS 보안성 보완
app.use('/tweets',tweetsRoute); // 라우팅 등록
app.use((req,res,next) => {
res.sendStatus(404); // 없는 경로를 호출 했을 때 처리
});
app.use((error,req,res,next) => {
console.error(error); // 에러 핸들링 - 최후 방어막 ㅎ_ㅎ
res.sendStatus(500);
});
app.listen(8080);
Tweets REST APIs – CRUD 뼈대 구성
라우터 (tweets.js)
import express from 'express';
import 'express-async-errors';
let tweets = [
{
id: '1',
text: 'Hello world!',
createAt: Date.now().toString(),
name: 'Dylan',
username: 'dylan',
url: 'https://cdn-icons-png.flaticon.com/512/3576/3576887.png'
},
{
id: '2',
text: 'Hello world!',
createAt: Date.now().toString(),
name: 'Bob',
username: 'bob',
url: 'https://cdn-icons-png.flaticon.com/512/3576/3576887.png'
},
]; // 우선은 메모리에 저장
const router = express.Router();
// GET /tweets
// GET /tweets?username=:username
router.get('/',(req,res,next) => {
const username = req.query.username;
const data = username
? tweets.filter(tweet => tweet.username === username)
: tweets;
res.status(200).json(data);
});
// GET /tweets/:id
router.get('/:id',(req,res,next) => {
const id = req.params.id;
const tweet = tweets.find(tweet=> tweet.id === id);
if(tweet){
res.status(200).json(tweet);
}else {
res.status(404).json({message : `Tweet id(${id}) not found`});
}
});
// POST /tweets
router.post('/',(req,res,next) => {
const {text, name, username} = req.body;
const tweet = {
id : Date.now().toString(),
text,
createAt : new Date(),
name,
username,
}
tweets = [tweet, ...tweets];
res.status(201).json(tweet);
});
// PUT /tweets/:id
router.put('/:id',(req,res,next) => {
const id = req.params.id;
const text = req.body.text;
const tweet = tweets.find(tweet => tweet.id === id);
if(tweet){
tweet.text = text;
res.status(200).json(tweet);
}else {
res.status(404).json({message : `Tweet id(${id}) not found`});
}
});
// DELETE /tweets/:id
router.delete('/:id',(req,res,next) => {
const id = req.params.id;
tweets = tweets.filter(tweet=> tweet.id !== id);
res.sendStatus(204);
});
export default router;
Postman API runner test
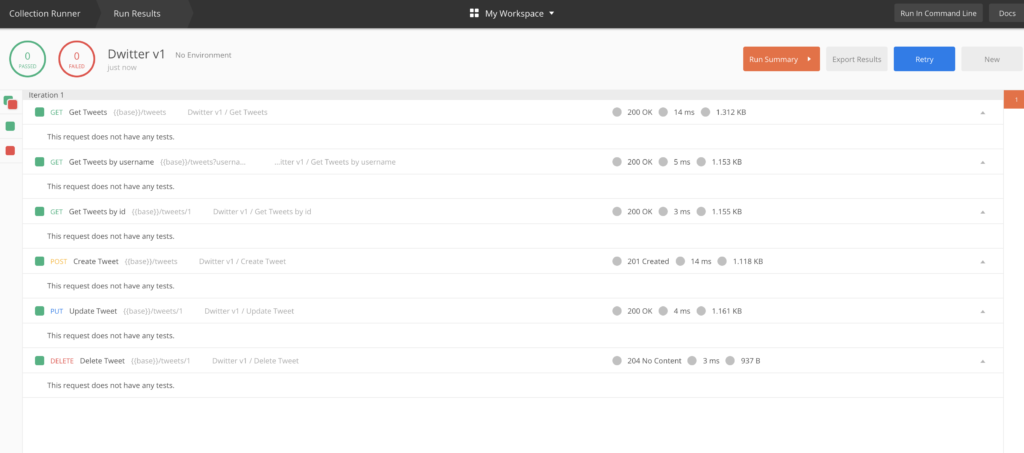
포스트맨은 collection 내에 요청들을 다 테스트해볼 수 있는 환경을 제공하는데, 지금까지 만든 요청들은 서버에서 잘 처리해줬음을 알 수 있다
프론트엔드 로직 (/src/service/tweet.js)
export default class TweetService {
constructor(baseURL){
this.baseURL = baseURL;
}
async getTweets(username) {
const query = username ? `?username=${username}` : '';
const response = await fetch(`${this.baseURL}/tweets${query}`,{
method : 'GET',
headers : {'Content-Type' : 'application/json'},
});
const data = await response.json();
if(response.status !== 200){
throw new Error(data.message);
}
return data;
}
async postTweet(text) {
const response = await fetch(`${this.baseURL}/tweets`,{
method : 'POST',
headers : {'Content-Type' : 'application/json'},
body : JSON.stringify({text, username: 'dylan', name: 'Dylan'}),
});
const data = await response.json();
if(response.status !== 201){
throw new Error(data.message);
}
return data;
}
async deleteTweet(tweetId) {
const response = await fetch(`${this.baseURL}/tweets/${tweetId}`,{
method : 'DELETE',
headers : {'Content-Type' : 'application/json'},
});
if(response.status !== 204){
throw new Error();
}
}
async updateTweet(tweetId, text) {
const response = await fetch(`${this.baseURL}/tweets/${tweetId}`,{
method : 'PUT',
headers : {'Content-Type' : 'application/json'},
body : JSON.stringify({text}),
});
const data = await response.json();
if(response.status !== 200){
throw new Error();
}
return data;
}
}
프론트엔드 코드 개선
위 프론트엔드 코드를 보면, 반복적으로 계속 사용되는 것들이 있다 
http 클래스 생성 (/src/network/http.js)
export default class HttpClient {
constructor(baseURL){
this.baseURL = baseURL;
}
async fetch(url, options){
const res = await fetch(`${this.baseURL}${url}`,{
...options,
headers: {
'Content-Type' : 'application/json',
...options.headers,
}
});
let data;
try {
data = await res.json();
}catch(error){
console.error(error);
}
if(res.status > 299 || res.status < 200){
const message = data && data.message ? data.message : 'Something went wrong!';
throw new Error(message);
}
return data;
}
}
코드 개선 (/src/service/tweet.js)
export default class TweetService {
constructor(http){
this.http = http;
}
async getTweets(username) {
const query = username ? `?username=${username}` : '';
return this.http.fetch(`/tweets${query}`,{
method : 'GET',
});
}
async postTweet(text) {
return this.http.fetch(`/tweets`,{
method : 'POST',
body : JSON.stringify({text, username: 'ellie', name: 'Ellie'}),
});
}
async deleteTweet(tweetId) {
return this.http.fetch(`/tweets/${tweetId}`,{
method : 'DELETE',
});
}
async updateTweet(tweetId, text) {
return this.http.fetch(`/tweets/${tweetId}`,{
method : 'PUT',
body : JSON.stringify({text}),
});
}
}
아주 깔끔해졌다